The recent Federal Reserve rate cut has sparked significant interest among consumers and investors alike. By lowering borrowing costs, this pivotal decision aims to stimulate economic activity, potentially leading to lower mortgage rates and enhanced debt relief for consumers struggling with various financial burdens. As the Fed adjusts its policy to support growth, the broader economy stands to benefit from the impacts of interest rates being recalibrated. This proactive stance could catalyze job creation and invest confidence into the market, fostering an environment ripe for recovery. With careful monitoring of inflation and employment trends, the Fed’s actions might very well shape the economic landscape in the months to come.
In a decisive move, the central banking system, commonly referred to as the Fed, recently implemented a noteworthy interest rate reduction. This maneuver is anticipated to yield positive repercussions for both everyday consumers and investors, particularly through improved loan affordability. As interest rates are driven lower, individuals may experience enhanced financial freedom, potentially resulting in increased spending that will invigorate growth across various sectors. The ramifications of this monetary policy change may also contribute to a more dynamic housing market, alleviating some of the pressures on consumers grappling with high mortgage and credit interest rates. Such strategic actions underscore the Fed’s commitment to maintaining a robust economic environment and ensuring that the financial health of Americans remains a priority.
Understanding the Implications of the Federal Reserve Rate Cut
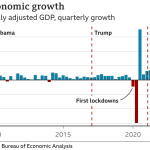
The recent rate cut by the Federal Reserve is poised to have significant implications for both consumers and the broader economy. By reducing the key interest rate by half a percentage point, the Fed aims to stimulate economic activity amid concerns about inflation and growth. This decision is particularly impactful as it marks the first reduction in four years, signaling a shift in monetary policy that could pave the way for additional cuts in the near future. As economist Jason Furman suggests, such a move can invigorate spending and borrowing, ultimately fostering a more robust economic environment.
However, the timing and effectiveness of these benefits remain uncertain. Consumers may soon see lower mortgage rates, which could enhance housing affordability, yet many remain burdened with high credit card and auto loan rates. The interplay between the Fed’s policy decisions and the subsequent consumer behavior will be critical in determining the overall impact of these rate cuts. The hope is that as borrowing costs decrease, more consumers will take advantage of the lower rates, leading to increased consumer spending, which is essential for economic growth.
The Effects of Rate Cuts on Mortgage Rates and Housing Affordability
As the Federal Reserve cuts rates, one of the most immediate effects can be observed in the mortgage market. Typically, lower interest rates translate to more favorable mortgage rates, which can help alleviate some of the housing affordability challenges faced by many homebuyers. With the expectation that the Fed will continue to ease policy, mortgage rates are likely to decrease further, allowing potential homeowners to secure loans at more manageable rates. This is particularly crucial in a housing market that has seen soaring prices in recent years.
Nonetheless, even with a reduction in rates, it is important to acknowledge that rates may not drop significantly compared to historical lows. The easing of borrowing costs is only one piece of the puzzle; the overall health of the job market and consumer confidence will also play vital roles in how effectively these lower rates unleash pent-up demand in the housing sector. As the Fed continues to recalibrate its policies, the interaction between lower mortgage rates and economic indicators will ultimately shape the landscape of the housing market.
The Broader Economic Effects of Federal Reserve Policy Adjustments
The Federal Reserve’s policy adjustments not only aim to stabilize inflation but also seek to influence overall economic growth. By cutting rates, the Fed encourages borrowing and investment, which can lead to job creation and economic expansion. Jason Furman highlights that while immediate effects may be muted, the longer-term outlook could include increased job opportunities and growth as businesses respond to lower borrowing costs. This is particularly evident in sectors sensitive to interest rate changes, such as real estate and consumer lending.
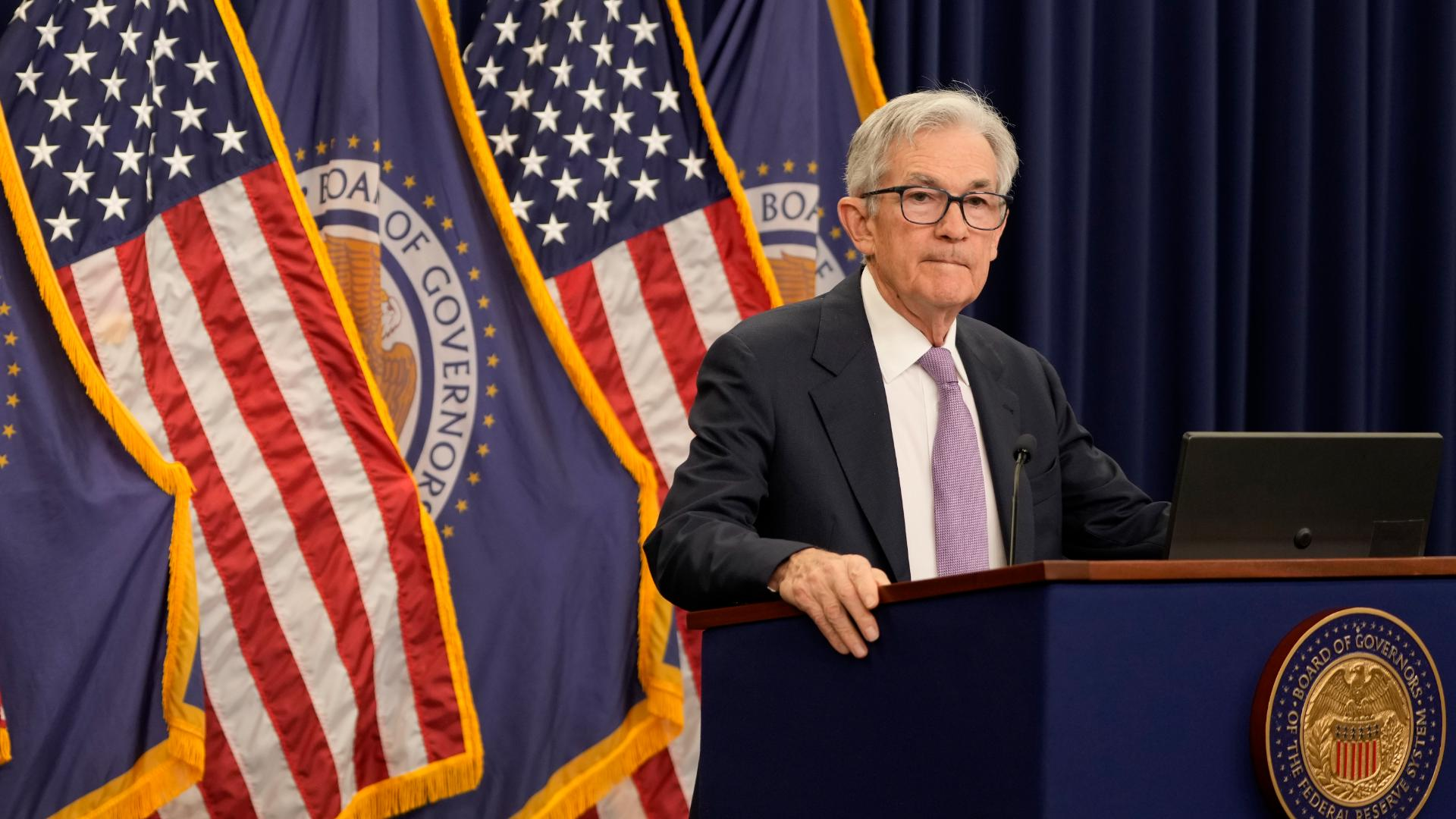
Moreover, the Fed’s approach signifies a commitment to monitoring economic indicators closely. The potential for additional rate cuts, as indicated by Fed Chairman Jerome Powell, reflects an adaptive strategy to respond to economic data. Should the labor market show signs of deterioration, the Fed is prepared to enact further cuts, instilling a sense of stability in the market. As businesses and consumers navigate this landscape, understanding the implications of these Fed decisions becomes essential for making informed financial choices.
Debt Relief for Consumers: The Role of Rate Cuts
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut represents a crucial turning point for many consumers struggling with debt. For individuals carrying credit card balances and other high-interest loans, reduced rates can mean lower repayment costs and a clearer path to financial relief. As borrowing costs decline, the hope is that consumers will feel empowered to pay down existing debts more rapidly, which can ultimately lead to improved financial well-being.
However, consumers should remain cautious. While rates are expected to drop, many existing debts still carry higher interest rates than desirable. Thus, while the short-term implications of the Fed’s decisions are positive, consumers must also consider their financial management strategies to ensure they capitalize on the benefits of lower rates. This will require a careful assessment of personal finances and a commitment to reducing outstanding debts in a responsible manner.
Future Projections: The Economy Post-Rate Cuts
Looking ahead, the economy is likely to continue evolving in response to the Federal Reserve’s rate cuts. As mortgage and borrowing costs decrease, consumer spending is anticipated to rise, which can boost economic growth. However, the interplay between these factors and external economic conditions remains a crucial consideration. If inflation remains in check and employment data supports continued growth, the Fed may find itself in a favorable position to maintain or adjust rates as needed.
Nonetheless, there are inherent risks associated with this strategy. Should inflation resurface unexpectedly or if the labor market shows weakness, the Fed could be compelled to revise its course, potentially reinstating higher rates. Thus, while the current environment appears conducive to growth, it is essential for consumers and businesses alike to remain vigilant and prepared for the dynamic nature of the economy as shaped by ongoing Fed policy decisions.
Consumer Sentiment and Expectations Following Rate Cuts
Consumer sentiment plays a vital role in shaping economic outcomes, especially following significant monetary policy changes like the Federal Reserve rate cut. As confidence in the economy grows, consumers are likely to increase spending, which can further stimulate economic activity. The positive outlook from the Fed regarding inflation could bolster consumer confidence, leading individuals to take on loans for major purchases such as homes or vehicles.
However, maintaining this momentum requires constant monitoring of economic indicators. If consumers grow optimistic about their purchasing power, it can lead to increased debt levels, which may undermine the objectives of the rate cuts if not managed carefully. Thus, understanding the intricate relationship between consumer sentiment and the effectiveness of the Federal Reserve’s policies is crucial for projecting future economic trends.
The Balance Between Growth and Inflation: A Delicate Dance
Navigating the balance between stimulating economic growth and controlling inflation is a recurring challenge for the Federal Reserve. The recent half-point rate cut reflects the Fed’s commitment to encouraging growth in the face of potential economic slowing down. By lowering borrowing costs, the Fed aims to spur investment and consumer spending while keeping inflation in check. This delicate dance requires ongoing analysis and adjustments based on incoming data, as highlighted by Chairman Powell’s remarks.
As the Fed implements these rate cuts, the impact on inflation will be closely monitored. While the goal is to foster economic growth, excessive stimulus can lead to rising prices if demand outstrips supply. Hence, the Fed’s strategy will depend on maintaining an equilibrium that fosters sustained growth without igniting inflationary pressures. Stakeholders across the economy should remain attuned to this balance as the Fed signals its intentions through policy adjustments.
Long-Term Implications of Federal Reserve Rate Policy
The long-term implications of the Federal Reserve’s rate cuts extend far beyond immediate consumer benefits. For instance, businesses may find a more conducive environment for expansion as borrowing costs decrease, potentially leading to an overall increase in employment opportunities. This shift can further strengthen the economy, creating a virtuous cycle of growth and investment. According to economists, sustained low-interest rates can also encourage innovation and entrepreneurship, thereby bolstering economic resilience.
However, it is important to approach these changes with caution. Structural adjustments in the economy may take time to materialize, and the potential risks of prolonged low rates, such as asset bubbles or misallocation of resources, cannot be overlooked. Stakeholders must remain vigilant to ensure that the benefits of rate cuts do not lead to adverse long-term consequences that could impede growth and stability.
Consumer Strategies in a Low-Rate Environment
In the wake of Federal Reserve rate cuts, consumers are presented with diverse financial strategies to maximize benefits. With borrowing costs declining, now may be a prime time to refinance existing loans or take on new credit for significant purchases. By lowering interest payments, consumers can free up resources for savings or investment, creating opportunities for improved financial stability. It’s essential for consumers to proactively assess their financial situations to capitalize on these shifts.
Nonetheless, amidst these opportunities, consumers must also remain prudent in managing their debts. As rates come down, extending repayment terms can be tempting, but this should be balanced with a careful examination of long-term financial goals. Engaging in responsible borrowing and avoiding the pitfalls of accumulating unnecessary debt will be critical for navigating the low-rate environment effectively. A strategic approach will enable consumers to leverage the benefits of reduced borrowing costs while safeguarding their financial futures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of the Federal Reserve rate cut on the economy?
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut is expected to stimulate economic growth by lowering borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. It aims to encourage spending and investment, which can lead to increased job creation and overall economic activity. However, the full impact may take time to materialize as consumers adjust to changed interest rates.
How will the Federal Reserve rate cut affect mortgage rates?
The Federal Reserve rate cut is likely to lead to lower mortgage rates as lenders adjust their rates in response to the reduced cost of borrowing. This decrease in mortgage rates can enhance housing affordability, benefiting homebuyers and potentially easing the housing market crisis.
Can consumers expect debt relief after the Federal Reserve rate cut?
Following the Federal Reserve rate cut, consumers may experience some debt relief as interest rates on credit cards, car loans, and mortgages decrease. However, it’s essential to recognize that not all rates will drop immediately and the extent of relief can vary based on individual financial situations and market conditions.
What are the implications of the Federal Reserve policy for credit card debt?
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut can have positive implications for credit card debt by reducing the interest rates charged on outstanding balances. As a result, consumers may find it easier to manage and pay off their credit card debt, contributing to greater financial stability.
How does the Federal Reserve rate cut signal future economic policy direction?
The Federal Reserve rate cut indicates a shift toward a more accommodative monetary policy, suggesting that the Fed is closely monitoring economic conditions and is prepared to take further action if necessary. This proactive stance aims to sustain economic growth and mitigate potential downturns.
What effect does the Federal Reserve rate cut have on overall economic growth?
The Federal Reserve rate cut is intended to stimulate overall economic growth by lowering borrowing costs, which encourages spending by consumers and investment by businesses. In the long term, this can lead to job creation, increased demand for goods and services, and improved economic performance.
Will the Federal Reserve continue to cut rates through the year?
Based on current forecasts, the Federal Reserve may implement additional rate cuts throughout the year. However, this is contingent upon ongoing economic data and indicators, including inflation and labor market conditions.
How do lower interest rates affect consumers’ spending behavior?
Lower interest rates from the Federal Reserve typically encourage consumers to increase spending by making loans, such as mortgages and car loans, more affordable. This can lead to higher consumer confidence and spur economic growth.
What are potential risks associated with the Federal Reserve rate cut?
While the Federal Reserve rate cut may boost short-term economic activity, potential risks include increased inflation and asset bubbles if the cuts stimulate excessive borrowing and spending. Maintaining a balance between growth and inflation will be crucial.
How does the Federal Reserve rate cut relate to economic recovery strategies?
The Federal Reserve rate cut is a central part of economic recovery strategies, aimed at stimulating growth and ensuring stability in the financial system. By making borrowing cheaper, the Fed seeks to support consumers and businesses during uncertain economic times.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Federal Reserve Rate Cut | The Fed cut rates by 0.5% on September 18, 2024 – the first cut in four years. |
| Impact on Consumers | Consumers can benefit from lower mortgage rates, credit card debts and loans; timing remains uncertain. |
| Potential for Future Cuts | Fed Chairman Powell hinted at possibly two more cuts by year-end, depending on economic data. |
| Effects on Economy | Increased job creation and slight economic growth expected over the next 6-12 months. |
| Housing Market Impact | Continued decrease in mortgage rates anticipated, improving housing affordability. |
| Consumer Debt Relief | Debt relief remains uncertain; rates may not return to pre-pandemic lows. |
Summary
The Federal Reserve rate cut is a significant move that aims to boost the economy and support consumers struggling with debt. As mortgage rates are expected to decrease amid ongoing fiscal adjustments, both consumers and investors may see gradual improvements in their financial circumstances. However, the timing of these benefits is still uncertain, making it crucial for stakeholders to closely monitor future economic data and Fed announcements.