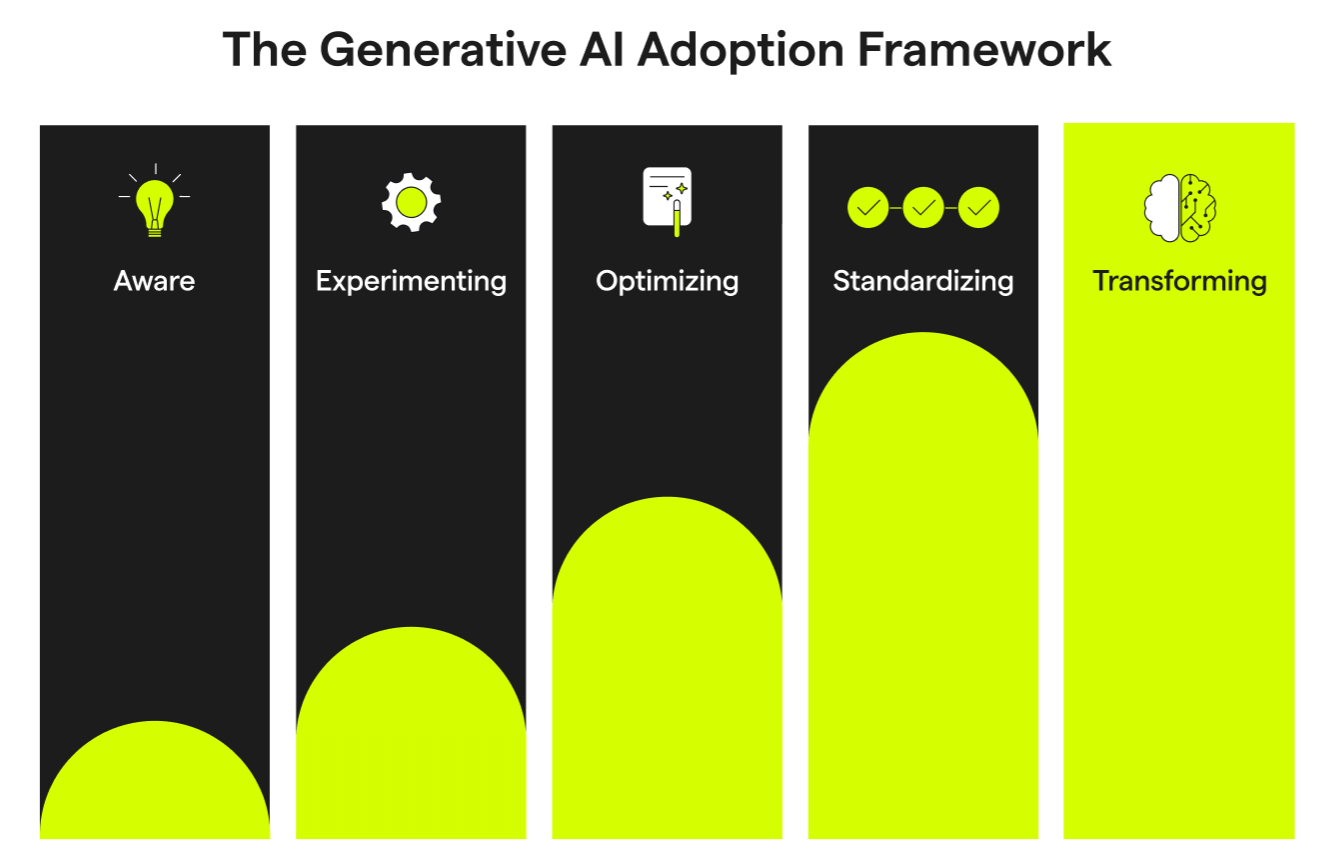
Generative AI adoption is rapidly transforming how we interact with technology, far exceeding the embrace of the internet and personal computers. As almost 40% of U.S. adults engage with this innovative tool, businesses are beginning to unlock the potential of AI technology adoption in their operations. Its impact on workplace AI tools is reshaping tasks from email composition to data management, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. Moreover, understanding AI usage in America reveals significant demographic insights that highlight disparities in adoption rates, particularly across age and educational backgrounds. As organizations harness the business applications of AI, they stand on the cusp of profound economic shifts driven by this cutting-edge technology.
The swift uptake of artificial intelligence tools, particularly in workplace environments, has sparked a new era of technological integration. This evolution, often referred to as the integration of intelligent automation, is marked by its rapid implementation across various sectors, indicating a sophisticated understanding of how tools like ChatGPT and others can enhance productivity. The exploration of AI’s implications reveals a landscape where digital transformation is no longer a goal but a necessity for competitive advantage. As professionals navigate the nuances of AI-driven solutions, it’s essential to analyze how these tools can be optimized for business effectiveness. The overarching influence of intelligent technology is setting the stage for significant advancements in operational methodologies across industries.
The Rapid Adoption of Generative AI Technology
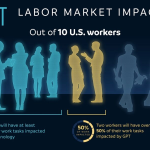
The adoption of generative AI technology has surged at a remarkable pace, surpassing the initial embrace of personal computers and the internet. As of August 2024, nearly 40 percent of American adults reported utilizing generative AI tools such as ChatGPT. This rapid uptake is indicative of the integration of generative AI into daily life and work, underscoring its role as a transformative force in both personal and professional environments. Economists and technology experts are keen to analyze this trend, as the speed and extent of a technology’s adoption often correlate with its future economic impact.
What sets generative AI apart from earlier technological waves is its accessibility and the fact that it builds on a foundation created by prior innovations. In contrast to the high costs and limited availability of early PCs and the internet, generative AI is being effortlessly incorporated into existing workflows, making it a stimulant for productivity. As companies begin to recognize this potential, strategies that integrate generative AI into operational frameworks are becoming increasingly vital for maintaining competitive advantages in the marketplace.
Impact of Generative AI on Business Applications
The impact of generative AI on business applications is multifold, with AI tools increasingly being used for tasks ranging from automating repetitive tasks to enhancing decision-making processes. Nearly 28 percent of employed individuals reported using AI technologies at work, illustrating how businesses are capitalizing on the capabilities of generative AI to streamline operations. The tools facilitate more efficient communication, data analysis, and content generation, enabling teams to focus on higher-level strategic initiatives.
Moreover, the implications of generative AI extend beyond mere workflow efficiency; they encompass the potential for creating entirely new business models and revenue streams. For instance, sectors that are early adopters of generative AI may find themselves at a significant advantage, as they can leverage AI-driven insights to forecast trends, optimize customer experiences, and innovate their service offerings. As generative AI technology continues to evolve, its role in shaping the future of business will likely become even more pronounced.
Demographic Trends in AI Usage
Notably, demographic factors significantly influence the rate at which generative AI is adopted across various segments of the workforce. Younger individuals and those with higher education levels are at the forefront of generative AI usage, reflecting a generational shift in technology adoption. This trend mirrors past technologies, as younger populations tend to embrace new tools more readily. For businesses, understanding these demographic trends is crucial for tailoring AI initiatives that maximize utility and engagement.
Gender disparities in AI usage are also noteworthy, as studies have indicated that men, especially in STEM fields and managerial roles, are more likely to utilize generative AI tools than their female counterparts. While earlier technological waves saw women engaging more with PCs due to their prevalence in administrative roles, the widespread applicability of generative AI across various industries introduces a new dynamic. Companies that aim for inclusive AI adoption strategies need to address this disparity to ensure diverse talent can fully leverage the potential of AI technology.
Generative AI Versus Traditional AI Tools
While traditional AI tools have paved the way for automation in various fields, generative AI represents a leap forward by not only performing tasks but also creating content and providing insights in a more human-like fashion. The difference lies in the fact that generative AI can synthesize information and generate unique outputs, making it a versatile tool for creative problem-solving. This innovation broadens the scope of AI applications, allowing organizations to harness AI tools beyond rote mechanistic tasks.
The ability to create new content also opens opportunities for collaboration between human intelligence and generative AI, enhancing brainstorming sessions and creative processes in industries such as marketing, design, and software development. As businesses recognize the unique capabilities offered by generative AI, they are likely to integrate these tools into their workflows, fundamentally changing how tasks are executed and driving innovation in product development.
Implications for the Future Workforce
The integration of generative AI into the workspace is set to redefine job roles and the overall composition of the workforce. As AI tools become more proficient at managing tasks traditionally held by humans, a shift towards a more collaborative work environment, where humans and AI work in tandem, is anticipated. This necessitates a reevaluation of skills required in the modern workplace, with a growing emphasis on digital literacy and adaptability to new technologies.
Furthermore, the demand for employees who can effectively interact with and guide AI systems will likely increase. Companies may focus on training their workforce on how to harness generative AI tools to enhance productivity and creativity. Retraining and upskilling initiatives will be essential to ensure that the workforce can adapt to these new technologies, thus reducing potential job displacement while fostering an innovative company culture.
Generative AI in Remote Work Settings
The rise of remote work has provided a fertile ground for the adoption of generative AI technologies. As teams navigate the challenges of collaboration from various locations, AI tools offer solutions that enhance communication, scheduling, and project management. For instance, generative AI can draft emails, summarize meetings, and even assist in creating presentations, allowing remote workers to maintain high levels of productivity amidst geographical obstacles.
Moreover, the flexibility of generative AI tools means that they can be customized to suit the specific needs of remote teams, making them invaluable assets in achieving seamless collaboration. Companies that leverage generative AI within their remote work strategies are more likely to attract top talent by providing them with the tools necessary to excel in a virtual working environment, thus enhancing overall job satisfaction and performance.
The Role of AI Education in Adoption
As generative AI technology continues to evolve, the importance of education in AI adoption becomes increasingly apparent. Educational institutions and workforce training programs play critical roles in equipping individuals with the necessary skills to effectively utilize AI technologies. Integrating AI education into curriculums can foster a generation adept at leveraging these tools for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Moreover, companies that prioritize ongoing education and training in generative AI technologies will likely retain their competitive edge. Encouraging employees to pursue professional development in AI can enhance a company’s overall productivity as workers become more adept at navigating and utilizing these emerging technologies, ultimately driving performance and growth.
Challenges in Implementing Generative AI
Despite its potential, the implementation of generative AI poses several challenges that organizations must address. Issues related to data privacy, ethical use, and cybersecurity need to be meticulously managed to safeguard against misuse and to foster trust among users. Businesses must establish clear guidelines regarding the responsible use of AI tools to mitigate risks while promoting innovation.
Additionally, alignment between human decision-making and AI capabilities will be crucial in ensuring successful integration. Striking a balance between leveraging generative AI for insights and maintaining human oversight will enable organizations to harness the full potential of these technologies while minimizing drawbacks. Through careful planning and regulatory compliance, businesses can navigate these challenges effectively.
Exploring the Economic Impact of Generative AI
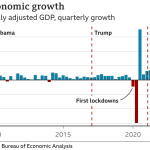
The economic impact of generative AI is anticipated to be profound, reshaping industries and creating new markets. As seen in previous technological revolutions, early adopters of generative AI may gain significant competitive advantages, leading to growth and profitability. The potential for reduced operational costs and enhanced efficiency will likely drive businesses to explore innovative applications of generative AI, potentially resulting in job creation in sectors aligned with AI development.
Moreover, as generative AI matures, it will likely catalyze further advancements in related technologies, leading to synergies that amplify overall economic growth. By identifying and leveraging the business applications of AI, organizations can stay ahead in an increasingly technology-driven marketplace, thus contributing to the overall evolution of the economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current rate of generative AI adoption among American workers?
As of August 2024, nearly 40% of American adults aged 18-64 reported using generative AI technologies, such as ChatGPT, for various tasks both at work and home. Specifically, 28% stated they utilized these tools in their workplace.
How does generative AI adoption compare to the adoption of personal computers and the internet?
Generative AI adoption is occurring at a significantly faster pace compared to the internet and personal computers. In its early stages, generative AI reached a usage rate of nearly 40%, whereas the internet and PCs only achieved approximately 20% adoption after two years and three years, respectively.
Which sectors are leveraging generative AI technology the most in the workplace?
Generative AI is predominantly used in STEM and management positions, where usage rates tend to be higher. However, it is worth noting that adoption is widespread across various occupations, including blue-collar jobs, indicating its versatility and growing importance in multiple industries.
What are some common tasks where workplace AI tools like generative AI are utilized?
In the workplace, generative AI tools are often utilized for tasks such as drafting emails, generating reports, conducting research, and automating routine processes, enhancing productivity across various job functions.
What factors contribute to the swift adoption of generative AI in the U.S.?
Several factors contribute to the rapid adoption of generative AI, including the availability of foundational technologies like personal computers and the internet, which facilitate its integration into daily tasks. Additionally, the versatility of generative AI makes it attractive for a wide array of applications.
How does generative AI usage vary across different demographic groups?
Usage of generative AI tends to vary significantly by demographic, with younger individuals, those with higher education levels, and men showing higher adoption rates. This pattern mirrors previous technology adoption trends where familiarity and education play vital roles.
Why should businesses focus on generative AI adoption now?
Businesses should prioritize generative AI adoption because it is increasingly seen as a foundational technology for future innovations. Those who effectively harness generative AI now stand to gain a competitive edge, capitalizing on opportunities for efficiency and new business models over the next decade.
What implications does the influx of generative AI have on the future of workplace AI tools?
The adoption of generative AI indicates a shift towards more integrated and intelligent workplace AI tools. Companies that develop applications leveraging generative AI will likely see significant benefits, leading to the emergence of innovative solutions and transformative changes in business operations.
How does the impact of generative AI reflect broader trends in AI usage in America?
The rise of generative AI is part of a broader trend of increasing AI technology adoption across America. As generative AI showcases potential benefits in productivity and creativity, it is paving the way for more widespread acceptance and utilization of AI solutions across various sectors.
What should executives keep in mind regarding generative AI for the future?
Executives should recognize that generative AI represents a pivotal moment for technology in the workplace. Understanding its capabilities and exploring innovative applications can lead to significant advancements and profitability as this technology continues to evolve and integrate into business practices.
| Key Points | Generative AI Adoption Rate | Demographics of Usage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generative AI being adopted faster than both the internet and personal computers. | |||
| 40% of U.S. adults (aged 18-64) have used generative AI technologies. | 28% of employed adults used it at work. | ||
| Higher usage rates observed among younger individuals, men, and those with higher education levels. | Usage is prevalent across various job sectors, particularly in STEM and management. | ||
| Study reveals swift adoption alongside existing technologies (PCs, internet). | |||
Summary
Generative AI adoption is transforming the workforce at an unprecedented pace, surpassing both the internet and personal computers. With nearly 40% of Americans utilizing generative AI tools, this technology has become integral in various sectors, enhancing productivity and innovation. As businesses recognize the trend, the importance of early adoption becomes clear. Understanding and leveraging generative AI will undoubtedly dictate the competitive landscape in the years to come.