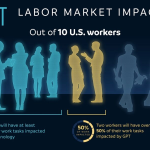
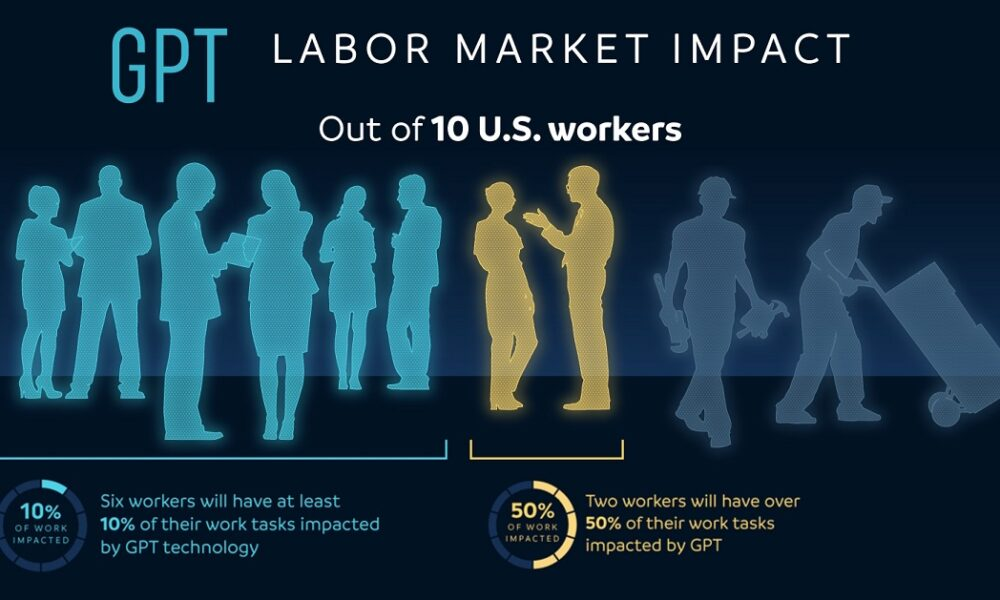
The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming undeniably profound as companies increasingly integrate advanced technologies into their operations. A recent study highlights how automation in the workforce is reshaping job dynamics and creating unprecedented trends in employment. As AI labor market disruption unfolds, we witness significant shifts, including changes in the prevalence of various professions and wage distributions. With an ongoing occupational churn, the future of work with AI raises questions about the sustainability of traditional roles and skill requirements. As AI continues to evolve, its influence could dramatically transform technology and jobs, prompting workers and industries alike to adapt to a new economic reality.
The influence of artificial intelligence on employment sectors is a topic generating considerable discussion, particularly regarding its role in workforce evolution. As innovations in machine learning and automation permeate various industries, a notable phenomenon known as occupational turnover has emerged, reshaping available job landscapes. This ongoing evolution signals a shift in the roles and responsibilities that define the workplace of tomorrow, compelling individuals to harness new skills and adapt to an increasingly digitized environment. The transformation led by AI has sparked debates about the viability of existing positions while offering exciting prospects for future job creation. Ultimately, understanding how these technological advancements correlate with shifts in employment is essential for navigating the changing tides of the modern labor market.
Understanding AI’s Impact on the Labor Market
The emergence of artificial intelligence is significantly transforming the labor market, sparking discussions on its implications for employment and economic dynamics. A recent study highlights that AI is not only reshaping how work is performed but also altering the distribution of jobs within various industries. As companies increasingly adopt AI technologies, the demand for skilled labor may outpace the supply, leading to potential labor shortages in technical fields while displacing less skilled jobs. This substantial shift reflects a growing trend of AI labor market disruption, challenging workers to adapt and acquire new skills to remain relevant.
The findings from the research reveal that while AI has the potential to create jobs, it may favor those with higher skill levels, leaving low-skilled workers vulnerable to unemployment. With the ongoing introduction of automation in the workforce, tasks previously done by humans are now being handled by machines, leading to occupational churn. This phenomenon indicates a transition in employment patterns where lower-wage positions diminish, while roles in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) are on the rise. The labor market is evolving, pressing for a reevaluation of educational and training programs to equip workers for future demands.
The Role of Automation in Job Displacement
As automation technologies become more sophisticated, the risk of job displacement has risen significantly. A historical perspective shows that technological advancements have continuously disrupted labor markets, but the current wave of automation, fueled by AI, appears to be occurring at an unprecedented rate. Professionals in various sectors, particularly those in repetitive tasks, need to recognize the potential for their roles to be automated. The impact of automation in the workforce is manifested in declining employment rates in several sectors, particularly retail and low-skill service sectors, where the need for human workers is rapidly diminishing.
Researchers have pointed out that the effect of automation is not uniformly negative; it offers the potential for increased productivity and efficiency. However, the downside includes an exacerbated divide between high- and low-income jobs. The fear of ‘automation anxiety’ observed in past decades is resurfacing, prompting a call for urgent adaptations in workforce management and reskilling initiatives. Educators and policymakers are urged to foster environments where lifelong learning is prioritized, enabling workers to transition to emerging roles that leverage automation to enhance productivity.
Emerging Trends in Labor Due to AI and Automation
The recent studies identified key trends driven by AI and automation that are reshaping the labor landscape. One of the observed trends is the phenomenon of job polarization, characterized by job growth at both ends of the wage spectrum while middle-wage jobs decline. This shift suggests that as AI continues to integrate into various industries, the demand for high-skilled positions will increase, reinforcing the need for specialized training. Moreover, the rising proportion of STEM jobs echoes the need for workers proficient in navigating and utilizing new technologies, reinforcing the importance of education in these fields.
Additionally, there is a noticeable decline in low-skill jobs, particularly in sectors that are increasingly automated. For instance, the retail industry has seen a significant reduction in sales positions, largely due to the growth of e-commerce and the adoption of predictive AI technologies. As consumers shift their buying habits online, the traditional retail workforce may face irrelevance unless they pivot to roles that cannot be automated. Understanding these trends is critical for both workers and businesses to prepare for future workforce demands and to ensure effective solutions for labor market disruptions.
Skills Gap and the Future of Work with AI
With the rapid integration of AI in the workplace, a widening skills gap has emerged, revealing the urgent necessity for workers to upskill and reskill. As automation reshapes job requirements, productivity expectations for knowledge workers are on the rise. The demand for abilities that complement AI technologies, such as data analysis, critical thinking, and technology management, are now more critical than ever. Companies are not only seeking individuals who have technical proficiency but also those who can adapt to the evolving technological landscape with agility and innovation.
Employers are increasingly recognizing the need for collaborative talent that complements AI rather than competes with it. The future of work with AI indicates a paradigm shift towards roles that require human ingenuity and creativity. To thrive in this new environment, both academic institutions and businesses must work hand-in-hand to cultivate a workforce that embraces continuous learning. Organizations should prioritize investing in training programs that equip employees with essential skills, fostering a culture that values adaptation and growth in the face of technological advancements.
Addressing Employment Volatility and Economic Stability
The fluctuations observed in the labor market, termed employment volatility, can be attributed to the disruptive nature of technology, particularly AI. Historical data suggests that periods of significant technological advancement often come with heightened uncertainty in job security, leading to concerns about economic stability. The labor market’s response to these disturbances emphasizes the delicate balance between embracing innovation and safeguarding workers from potential obsolescence. Understanding this volatility is crucial for policymakers and business leaders as they navigate these changes.
To address the challenges posed by employment volatility, proactive measures must be implemented to support affected workers. Economic policies that encourage investment in workforce development and retraining initiatives can mitigate the adverse impacts of job displacement. Furthermore, providing safety nets for affected individuals can help ease the transition into new roles. Creating an adaptable workforce that can withstand the pressures of technological advancements is vital for ensuring long-term economic stability amid the dynamic changes driven by AI and automation.
Navigating the Challenges of Job Polarization
Job polarization has become a prominent theme in discussions about the future of work, particularly as AI and automation continue to reshape the labor landscape. This phenomenon is characterized by the simultaneous growth of high-wage and low-wage job categories, while middle-wage jobs stagnate or decline. The implications of job polarization extend beyond individual job loss; it signifies a broader economic transition that can lead to increased inequality and social tension. To counteract these effects, it is essential to understand the dynamics at play and take strategic actions to address these imbalances.
By investing in training programs focused on skill acquisition for middle-wage roles, businesses and governments can help bridge the gap created by this polarization. Upskilling workers for higher positions or transitioning them into essential services can not only enhance individual employability but also contribute to a more balanced labor market. As AI technologies evolve, seeing them as a catalyst for creating opportunities rather than threats can empower workers and foster positive growth in the economy.
The Rise of STEM Jobs in the AI Era
As artificial intelligence continues to permeate various sectors, the demand for jobs in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) has experienced a remarkable increase. The significant surge from 6.5 percent to nearly 10 percent of the workforce in STEM roles underscores a transition towards a technology-driven economy. This rise indicates that employers are actively seeking professionals capable of designing, implementing, and managing advanced technologies. The future of work rests heavily on these skill sets, making STEM education fundamental for sustained economic growth.
However, this impressive growth in STEM roles calls into question the accessibility of such positions for a broader workforce. Ensuring that educational pathways to these careers are equitable and inclusive is paramount. Initiatives targeting underrepresented groups in STEM can foster diversity in the field, leading to innovative solutions that benefit society as a whole. As the labor market continues to shift under the influence of AI, the emphasis on STEM jobs represents a crucial step towards adapting to the changing global economy and mitigating the potential negative effects of occupational churn.
Preparing for the Transition to AI-Enhanced Jobs
As the integration of artificial intelligence reshapes industries, preparing workers for AI-enhanced jobs becomes a priority. The nature of work will evolve with AI complementing human abilities, enhancing productivity while reducing the limitations of manual tasks. Workers must be increasingly adaptable, embracing continuous learning and flexibility to thrive in this new era. Companies should consider implementing sustainable training programs that foster a culture of learning and encourage employees to stay engaged with emerging technologies.
In addition to upskilling, fostering a mindset that welcomes change can empower workers to navigate this transition successfully. Collaborations between educational institutions, industry leaders, and governmental agencies can establish pathways for workers to develop necessary skills aligned with the demands of AI-enhanced roles. As we prepare for a workforce fundamentally altered by intelligent technologies, the focus should remain on creating supportive environments where employees feel motivated to pursue growth and adaptation.
The Importance of Lifelong Learning in the Age of AI
In the landscape shaped by AI and automation, the concept of lifelong learning has never been more crucial. As technologies continue to evolve at a rapid pace, workers must commit to ongoing education and skill development to remain competitive in the labor market. Educational frameworks that prioritize adaptability and resilience will empower individuals to embrace new challenges and seize emerging opportunities. Employers play a pivotal role in promoting lifelong learning by offering resources and support for continuous professional development.
The responsiveness of workers to changing market conditions hinges on their ability to acquire new skills swiftly. Emphasizing the importance of learning not only ensures that individuals retain their employability but also drives organizational success as companies adapt to technological advancements. A concerted effort towards fostering a culture of constant learning can bridge the skills gap, align workforce capabilities with market demands, and ultimately create a more robust labor market equipped to thrive amid the disruptions of AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI labor market disruption influencing job stability?
AI labor market disruption is significantly altering job stability by introducing fluctuations in occupational churn. The recent study by Harvard economists reveals that while stability characterized the 1990-2017 period, trends since 2019 indicate a dramatic shift in job dynamics due to AI advancements.
What trends indicate the future of work with AI?
The future of work with AI is marked by four key trends: 1) an end to job polarization favoring high-skilled roles; 2) a surge in STEM job growth; 3) declining low-paid service sector employment; and 4) significant reductions in retail jobs, driven largely by technology adoption and AI integration.
How does automation in the workforce affect employment opportunities?
Automation in the workforce is reshaping employment opportunities by favoring higher-skilled positions while decreasing jobs in low-paid service areas. This trend suggests that as AI technology evolves, the labor market will continue to see significant changes, particularly in job availability across various sectors.
Is the concern about technology and jobs valid in the AI era?
Concerns surrounding technology and jobs are valid, particularly in the context of AI’s influence on employment. Researchers found that while previous fears about job displacement were overstated, recent evidence indicates that AI is starting to significantly impact job distribution and retention in various fields.
What is occupational churn, and how does it relate to AI’s impact on the labor market?
Occupational churn refers to the rate at which workers change jobs within the labor market. The impact of AI on occupational churn is becoming evident, as the recent trends suggest that AI is contributing to higher volatility in job roles, especially in technology-driven fields, reshaping the employment landscape.
How are investments in AI affecting job distributions in the labor market?
Investments in AI are reshaping job distributions by increasing demand for technical roles and diminishing opportunities in lower-skilled positions. The ongoing shift highlighted by Harvard’s research shows that AI technology is prompting firms to focus on higher-skilled positions while reducing reliance on low-paid jobs.
What types of jobs are at highest risk due to AI and automation?
Jobs in low-paid service sectors, particularly in retail and certain manual labor roles, are at the highest risk due to AI and automation. The study points to a significant decline in retail sales jobs attributed to the rise of e-commerce and predictive AI technologies.
How does AI enhance productivity while posing risks to job security?
AI enhances productivity by providing quicker solutions and more efficient processes, which can lead to greater output. However, this reliance on technology also poses risks to job security, as workers must adapt to technology demands and may find certain roles rendered obsolete.
| Key Points | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Overview: Co-authored by economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, the study examines AI’s impact on the U.S. labor market over the past century. | Historical Perspective: Analyzed 124 years of U.S. Census data to uncover trends of technological disruption and occupational churn. | Stability Period: A period of stability in job distribution was noted between 1990-2017, contrary to fears about robots replacing jobs. | Recent Trends: Post-2019 data shows significant shifts, with emerging trends driven by AI. | Job Polarization: Decline in job polarization, with more growth in well-paid jobs requiring high levels of training. | Growth of STEM Jobs: Increase from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024 for STEM-related roles. | AI Investments: Companies are increasing investments in AI, altering job distributions. | Decline in Low-Paid Jobs: Employment in low-paid sectors is declining, particularly in service industries post-2019. | Retail Job Losses: Retail sales jobs decreased from 7.5% to 5.7% of the job market between 2013 to 2023, exacerbated by COVID-19. | Long-term Implications: AI will empower certain jobs while displacing others, particularly in more traditional roles. | |
Summary
The impact of AI on the labor market is profound and multifaceted. As examined in a recent study, AI is not merely a technological advancement but a transformative force reshaping job distributions and creating new trends within the workforce. While historical data indicated a period of stability, the post-2019 era has shown significant changes driven by AI, affecting job polarization and leading to growth in high-paying positions at the expense of low-paid service roles. This dual effect of AI necessitates adaptation among workers and industries alike to leverage its benefits while mitigating displacement risks, changing the landscape of work as we know it.