Entrepreneurialism is redefining our workplaces and reshaping how we engage with our careers. Gone are the days when success was solely defined by traditional employment; instead, individuals are embracing diverse paths like freelancing and self-employment, mirroring the mantra to “Make Your Own Job.” This shift is a response to the evolving economy where work-life balance has become paramount. Now, more than ever, people are discovering the freedom and flexibility that comes with entrepreneurial ventures, allowing them to align their passions with profit. As we dive into the implications of this shift, it’s crucial to explore how entrepreneurialism influences our sense of purpose in the modern workforce.
The concept of entrepreneurial spirits extends beyond mere business ownership; it encompasses a broader spectrum of self-starters and innovators. This phenomenon is often referred to as the gig economy, where individuals take control of their careers through various forms of independent work, including freelancing and micro-enterprises. Many see this as a chance to escape the rigid confines of traditional jobs, elaborating on the need for a better work-life integration. Rather than merely existing in a corporate ladder, today’s entrepreneurs pursue creative projects that fulfill their professional and personal aspirations. As we explore this evolving landscape, understanding the nuances of these alternative pathways will shed light on the new dynamics of work and opportunity.
The Evolution of Entrepreneurialism in America
Entrepreneurialism has undergone significant transformations throughout American history, shaping the national landscape by altering how individuals perceive themselves in relation to work. This evolution began in the late 19th century during the industrial revolution when traditional employment structures began to decline. As technology advanced, many workers found themselves displaced, leading to an urgent need for alternative avenues of employment. The concept of “Make Your Own Job” emerged, encouraging individuals to harness their creative potential and leverage their skills to create opportunities for themselves rather than relying on conventional employment models.
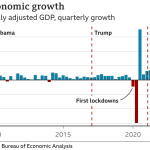
By examining the changes in the workforce, we see how entrepreneurialism flourished during economic hardships. The Great Depression, for instance, compelled many to turn to freelancing and other entrepreneurial ventures simply to survive. This shift not only redefined the job market but also laid the groundwork for modern self-employment practices. Today, we see a broader interpretation of entrepreneurialism that includes influencers, sidepreneurs, and gig workers, all contributing to a dynamic economy where the traditional employer-employee relationship has transformed into a more fluid interaction over job roles.
Freelancing: A Modern Path to Self-Employment
Freelancing has emerged as one of the most popular forms of self-employment in the 21st century, providing individuals with the flexibility to choose when and how they work. Unlike traditional employment, freelancing allows workers to carve out their career paths while also embracing work-life balance. Many freelancers have turned their passions—be it graphic design, writing, or digital marketing—into viable career options that offer financial independence and personal satisfaction.
The rise of digital platforms has facilitated this trend, enabling freelancers to connect with clients from around the globe. They now possess the ability to market their skills and services without the constraints of a conventional job. However, navigating the freelancing landscape also presents challenges, such as inconsistent income and the need for self-discipline. Yet for those who embrace this mode of work, freelancing exemplifies entrepreneurialism in action, showcasing how individuals can create jobs tailored to their lifestyles and aspirations.
Balancing Work and Life in an Entrepreneurial Age
In today’s entrepreneurial climate, achieving a healthy work-life balance can be challenging, especially for those who blur the lines between personal and professional lives. Many individuals who identify as entrepreneurs often feel pressured to work longer hours, driven by the desire to succeed in their ventures. This relentless pursuit can lead to burnout and stress, prompting a necessary conversation about the importance of self-care and leisure alongside productivity.
To foster a sustainable work-life balance, it is essential for entrepreneurs and freelancers to establish boundaries and prioritize their well-being. This includes setting specific work hours, designating spaces for work and relaxation, and making time for activities that recharge their minds and bodies. By recognizing the need for balance, individuals can maintain their creativity and motivation, ultimately leading to a more fulfilling entrepreneurial experience.
The Influence of Self-Employment on Personal Identity
Self-employment has significantly impacted personal identity, allowing individuals to express their values, creativity, and aspirations through their work. By creating their own jobs, many people experience a newfound sense of autonomy and empowerment that traditional employment often does not provide. This shift leads not only to a redefinition of success but also fosters a culture where individuals take pride in their unique contributions to the economy.
However, this identity shift also carries challenges, including societal expectations and the pressure to prove oneself as a viable entrepreneur. The journey of establishing a personal brand can be overwhelming, pushing many to navigate the complex landscape of entrepreneurship alone. Embracing the idea that self-employment is an ongoing journey can help individuals craft a more genuine connection between their work and identity, allowing them to thrive in their pursuits.
Challenging the Conventional Work Ethic
The rise of entrepreneurialism challenges traditional notions of the work ethic that once dominated American culture. The days where job security and corporate ladders dictated success are giving way to a new mindset that values innovation, creativity, and adaptability. This shift encourages individuals to rethink their approaches to work, shifting from a fixed perspective on success to a more fluid one that recognizes the importance of personal satisfaction and growth.
As a result, many are reconfiguring their career paths entirely, questioning what it means to be successful beyond financial gain. This new work ethic not only advocates for the celebration of risks and failures as integral steps toward growth but also emphasizes the importance of passion and purpose in all business endeavors. Challenging these old paradigms promotes an environment where skills can flourish, leading to diverse career paths and new opportunities.
The Role of Self-Help Literature in Shaping Entrepreneurial Mindsets
Self-help literature has played a crucial role in shaping the entrepreneurial mindset across generations. Influential works like Napoleon Hill’s “Think and Grow Rich” have inspired countless individuals to believe in their potential for success beyond traditional employment. These texts often emphasize the importance of specialized knowledge, self-marketing, and relentless determination, equipping readers with the psychological tools necessary to navigate the uncertain waters of entrepreneurship.
In this way, self-help literature does not just provide guidance but also acts as a motivational force that empowers individuals to take control of their destinies. By reinforcing the idea that one can ‘make their own job,’ these writings contribute to a culture that embraces innovation and encourages people to pursue their unique visions. As entrepreneurialism continues to evolve, so too will the literature that accompanies it, fostering a mindset of resilience and creativity.
Understanding the Risks and Rewards of Entrepreneurial Ventures
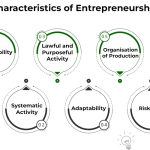
Entrepreneurial ventures come with inherent risks, often rooted in the unpredictability of the market and consumer demands. Individuals stepping into the realm of self-employment must be prepared for uncertainty and potential setbacks, similar to the challenges faced by any startup. However, acknowledging these risks is vital to cultivating a successful business mindset that embraces agility, learning from failures, and resilience.
The rewards, on the other hand, can be incredibly fulfilling—both financially and personally. Entrepreneurs often cite the joy of pursuing their passions, establishing their own work schedules, and connecting deeply with their customer base as significant benefits. Balancing the risks with the potential rewards is key for those engaging in entrepreneurialism, affirming that while difficult, the journey can lead to profound personal and professional growth.
The Impact of Technology on Freelancing and Entrepreneurship
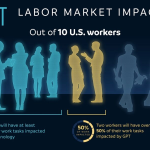
Technology has revolutionized the landscape of freelancing and entrepreneurship, enabling individuals to establish and manage their ventures from anywhere in the world. With digital tools and platforms available, entrepreneurs can effectively market their skills, communicate with clients, and track projects in real time, all of which contribute to increased productivity and efficiency. This transformation has allowed for a more diverse range of professions to thrive—from technology-driven startups to creative freelance projects—creating a vibrant gig economy.
However, the rapid advancement of technology also introduces new challenges. Competition has intensified as more individuals enter the freelance space, and the need for continuous skill enhancement is greater than ever. Additionally, the proliferation of digital workplaces often leads to a blurred line between work and personal life. As entrepreneurs navigate this changing environment, embracing technology effectively while maintaining a healthy work-life balance will continue to be crucial.
Future Trends in Self-Employment and Entrepreneurialism
Looking ahead, trends in self-employment and entrepreneurialism indicate a future where more individuals will embrace non-traditional career paths. The rise of remote work, coupled with evolving job markets, suggests a shift toward a more decentralized economy where independent careers will flourish. As the workforce becomes increasingly digital, opportunities will emerge for individuals to innovate and create their own job roles, aligning with their passions and values.
Additionally, emerging markets and evolving consumer demands will inspire new entrepreneurial ventures, creating a cycle of creativity and growth. The focus will continue to shift towards sustainable and socially responsible practices, while technological advancements will open doors for a diverse range of opportunities. As more individuals recognize the potential of entrepreneurship, we may see a continued democratization of the job market, paving the way for even more innovative business models that reflect the values of modern society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key components of entrepreneurship that fuel self-employment?
Entrepreneurship is pivotal to self-employment as it emphasizes innovation, risk-taking, and personal initiative. By leveraging unique skills and market opportunities, individuals can create their own paths, leading to a fulfilling career that prioritizes independence.
How does freelancing fit into the broader framework of entrepreneurialism?
Freelancing is a significant aspect of entrepreneurialism as it allows individuals to operate their own businesses without the constraints of traditional employment. It embodies the entrepreneurial spirit by enabling professionals to market their skills, control their schedules, and pursue projects that resonate with their passions.
What impact does entrepreneurialism have on work-life balance for self-employed individuals?
Entrepreneurialism often leads to a blurred line between work and personal life, especially for self-employed individuals. While it provides flexibility, it can also result in over-commitment and burnout as entrepreneurs strive to balance their ambitions with personal well-being.
In what ways does ‘Make Your Own Job’ illustrate historical shifts in entrepreneurialism?
‘Make Your Own Job’ highlights a historical shift where technological unemployment prompted a cultural embrace of entrepreneurialism. The book traces how economic challenges inspired Americans to adopt entrepreneurial practices, emphasizing self-reliance and the creation of opportunities amid declining job security.
What challenges do individuals face in adopting an entrepreneurial mindset in today’s economy?
Adopting an entrepreneurial mindset today can be challenging due to market volatility, technological disruption, and intense competition. Entrepreneurs must navigate these hurdles while fostering resilience and managing the stress associated with self-employment and the pressure to continually innovate.
How can aspiring entrepreneurs cultivate their work-life balance while pursuing their ventures?
Aspiring entrepreneurs can cultivate work-life balance by setting clear boundaries between work and personal life, prioritizing time management, and integrating regular self-care practices. This helps mitigate the relentless demands of entrepreneurialism and fosters a healthier approach to self-employment.
What role does self-help literature play in shaping perceptions of entrepreneurialism?
Self-help literature significantly shapes perceptions of entrepreneurialism by promoting values such as personal empowerment, innovative thinking, and continuous self-improvement. Works like ‘Think and Grow Rich’ encourage individuals to see their careers as extensions of their skills and creativity, thus fueling entrepreneurial ambitions.
How has the definition of entrepreneurialism evolved in response to economic changes?
The definition of entrepreneurialism has evolved from traditional business models to include diverse forms of self-employment and creative work. Economic shifts have led to a broader interpretation, encompassing various roles such as freelancers, managers, and intrapreneurs, who all contribute to dynamic entrepreneurial landscapes.
Why do some view entrepreneurialism as a ‘double-edged sword’ in modern society?
Entrepreneurialism is viewed as a ‘double-edged sword’ because, while it fosters innovation and job creation, it can also create anxiety and a sense of instability. The pressure to constantly succeed and adapt can lead to burnout, highlighting the need for balance in a rapidly changing economic environment.
What strategies can established entrepreneurs employ to thrive within their industries?
Established entrepreneurs can thrive by continuously innovating, networking, and staying attuned to market trends. Emphasizing adaptability and a willingness to learn can help them navigate challenges and sustain success in their entrepreneurial ventures.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Entrepreneurialism | Entrepreneurialism refers to the shift in work ethos towards self-initiative, creativity, and personal brand building. It encompasses various forms of entrepreneurship, including traditional founders, freelancers, and ‘intrapreneurs’. |
| Historical Context | The rise of entrepreneurialism can be traced back to the late 19th century, characterized by technological advancements leading to structural unemployment. It prompted a cultural shift towards personal ambition and job creation. |
| Cultural Shift | The ethos of ‘Make Your Own Job’ became prevalent, encouraging individuals to take charge of their careers rather than relying solely on traditional employment. |
| Influence of Self-Help Literature | Writers like Napoleon Hill popularized ideas around personal branding and specialized skill development, urging people to view their work in a new light. |
| Economic Impacts | Entrepreneurialism gained traction during economic downturns, with individuals pursuing self-employment as a means to cope with job scarcity. |
| Modern Implications | Today, entrepreneurialism thrives, supported by technology and a gig economy, fostering a culture of risk-taking and personal branding. |
| Mental Health Perspective | The relentless pursuit of entrepreneurial success can lead to anxiety and despair as individuals navigate a landscape filled with uncertainties. |
Summary
Entrepreneurialism represents a transformative force in work culture, reshaping how individuals engage with their careers and roles in society. The shift from traditional employment to a focus on self-initiative encapsulates a broader societal change, fostering creativity and personal investment in one’s professional journey. As articulated by Erik Baker in ‘Make Your Own Job’, this entrepreneurial drive can provide both opportunities and challenges, compelling individuals to navigate a landscape filled with uncertainties while striving for personal success.