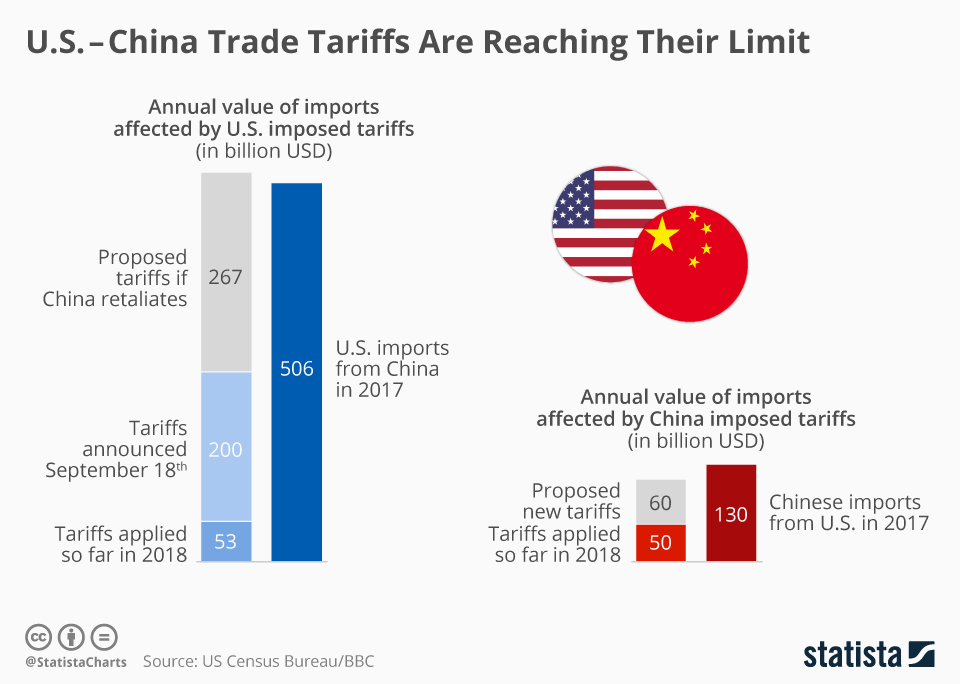
China tariffs have been a contentious issue, profoundly influencing the dynamics of US-China trade relations. As tensions rise and a potential trade war looms, the ramifications of imposing significant tariffs could extend far beyond mere economics. Experts warn that such measures might escalate prices for American consumers and disrupt supply chains critical to both American and Chinese economies. The implications of these tariffs could not only harm the China economy but could also prompt greater diplomatic estrangement between the US and its traditional allies. Understanding the tariff impact is essential for grasping the broader consequences of these trade policies on global markets and geopolitics.
Tariffs imposed on Chinese imports represent a significant shift in international trade policy and have the potential to redefine the economic landscape. As the US navigates its strategy for engaging with China, alternative terms such as import levies and trade barriers are pivotal in the dialogue surrounding these issues. Analysts predict that these financial restrictions could exacerbate tensions, leading to higher consumer prices and potential disruptions in various sectors. Moreover, the ongoing trade conflict could carry broader implications, affecting not just the Chinese market but also the intricate web of supply chains that connect economies worldwide. As stakeholders analyze these developments, understanding the fundamentals of trade protectionism and its fallout remains critical.
Understanding China Tariffs and Their Implications
The introduction of substantial tariffs on imports from China, as proposed by the U.S. government, stands to have profound implications on not only the economic landscape of China but also on American consumers and global trade dynamics. Analysts warn that tariffs ranging from 25% to as high as 60% could lead to increased prices on a wide range of goods, thus straining the budgets of everyday Americans. As the cost of imported products soars, consumers may find themselves facing elevated prices across sectors ranging from electronics to textiles, which could ultimately dampen domestic economic growth.
Additionally, these tariffs could stifle U.S.-China trade relations, pushing both nations into a contentious trade war that may affect diplomatic ties with traditional allies. Economists indicate that increased tariffs may lead to retaliatory measures from China, thereby exacerbating supply chain disruptions. Given that many U.S. companies rely heavily on Chinese-made goods or components, industries could face significant challenges in production and operations if tariffs lead to increased costs and reduced access to essential materials.
The Impact of Tariffs on Supply Chain Dynamics
Imposing high tariffs on Chinese imports is expected to disrupt established supply chains that American companies have relied upon for years. As tariffs increase costs, businesses may seek alternative suppliers or manufacturing partners, which would require significant adjustments in logistics and operations. This transition may not be seamless; finding new sources of supply in countries like Vietnam or India can be complex and time-consuming, thereby risking delays in production and fulfillment of goods.
Moreover, companies might face a dual challenge of balancing these increased operational costs while keeping prices competitive in the U.S. market. For example, industries heavily entrenched in high-tech manufacturing, such as semiconductors or consumer electronics, might struggle to find equivalent suppliers who can match the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of Chinese manufacturers. This could lead to longer lead times, reduced product availability, and potential increases in consumer prices, which underscores the far-reaching implications of a tariff-heavy approach.
China’s Economic Response to Potential Tariffs
Facing the prospect of aggressive tariffs, China is likely bracing itself for a complex set of economic challenges that could exacerbate its already sluggish growth. Beijing has historically relied on exports as a crucial component of economic stability; thus, the possibility of diminished access to U.S. markets raises concerns about maintaining a healthy trade surplus. Economists predict that China may need to pivot its focus towards enhancing domestic consumption and exploring new markets in regions like Southeast Asia and Latin America to offset potential losses in U.S. trade.
Furthermore, there are indications that the Chinese government may adopt strategic measures to mitigate the impact of tariffs on its economy, including the use of fiscal stimulus to boost domestic consumer spending. However, this could prove difficult as Chinese policymakers have traditionally favored a strong export-oriented strategy. The delicate balance between maintaining global trade ties and fostering internal economic resilience will be one of the biggest hurdles for China in the face of ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions.
The Geopolitical Ramifications of a Renewed Trade War
The reintroduction of tariffs could also reshape geopolitical alliances, as countries impacted by U.S. trade policies may seek to forge closer ties with China and each other. For instance, nations in the European Union, Australia, and Japan might find common ground with China as they all face trade restrictions imposed by the United States. This could lead to a significant shift in the existing geopolitical landscape and a potential weakening of the United States’ influence in global markets.
Additionally, a diversified network of trade partnerships may arise, pushing countries to collaborate with China in strategic sectors like technology, infrastructure, and energy. This shift could potentially isolate the U.S. and disrupt its role as a leader of the global trading system, further complicating its relationships with traditional allies. Such dynamics could also have long-term consequences, influencing how trade negotiations are approached and altering perceptions of economic policy alignment across the globe.
Long-term Effects on U.S.-China Trade Relations
The long-term effects of aggressive tariff policies could reshape the very foundations of U.S.-China trade relations, leading to a more complex and competitive landscape. If tariffs lead China to seek stronger economic relations with other nations, the shift in trade dynamics might create a less cooperative environment where both countries face off against each other more assertively. This change could hinder progress towards resolving trade disputes and make collaboration on issues like climate change and security more challenging.
Moreover, should the U.S. take a rigid approach with tariffs, it may inadvertently accelerate the process of de-coupling from China, which could weaken economic ties and strain global trade networks. In this scenario, businesses may resort to diversifying their supply chains, which could make them more resilient in the face of turmoil but may also incur higher costs and inefficiencies in the short term.
The Role of Alternative Markets in the Trade Landscape
As companies look beyond Chinese suppliers in response to increased tariffs, alternative markets are expected to gain prominence. Nations such as India, Vietnam, and others in Southeast Asia are well-positioned to attract investment as businesses explore new partnerships. However, these countries may not yet possess the breadth and depth of manufacturing capabilities established in China, leading to a challenging transition for many industries.
Furthermore, to effectively meet U.S. demand, these nations will need to invest significantly in upgrading their infrastructure, technology, and workforce. Although there is potential for growth, it is important to recognize that these markets face their own set of challenges, including regulatory hurdles and limitations in skill availability, which could hinder their ability to fully compensate for a decline in Chinese imports.
Examining Labor Shortages in the Context of Tariffs
The implementation of tariffs may exacerbate existing labor shortages in the U.S. economy, particularly in industries that are heavily reliant on Chinese imports. Increased costs and disruptions in the supply chain could deter companies from hiring or maintaining their workforce, leading to stagnation in job growth in sectors such as manufacturing and retail. As higher prices for goods and services begin to hit consumers, companies may also be forced to reassess their staffing needs, impacting overall economic stability.
Moreover, the uncertainty surrounding the long-term implications of tariffs may also contribute to a cautious hiring environment, where businesses hesitate to expand their workforce until the trade landscape stabilizes. This situation could lead to a cycle of limited economic growth, where both supply and labor are constrained by ongoing trade tensions and market unpredictability, underscoring the broader ramifications of tariff policies.
The Future of U.S.-China Relations Beyond Tariffs
As tariff discussions unfold, the future of U.S.-China relations remains uncertain. Analysts suggest that moving beyond tariffs to engage in meaningful dialogue could pave the way for more constructive trade relations, ultimately benefiting both nations. Establishing cooperative frameworks around shared economic interests may provide a path toward lessening tensions and fostering a collaborative approach to addressing global challenges.
Moreover, a shift from a confrontational stance to one focused on mutual benefits may encourage both countries to explore strategic partnerships in areas such as technology, climate change, and international security. By prioritizing diplomacy over economic isolation, the U.S. and China could foster a more stable and prosperous global economy, paving the way for mutually beneficial outcomes in their ongoing trade relationship in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How could the new China tariffs affect US-China trade relations?
The impending China tariffs could significantly strain US-China trade relations by elevating tensions and leading to retaliatory measures. Increased tariffs on Chinese goods may result in higher prices for American consumers and could hinder diplomatic ties, making negotiations more challenging.
What are the potential impacts of China tariffs on the US economy?
The China tariffs may trigger inflation, leading to higher costs for consumers and disruptions in supply chains. As US companies depend on Chinese imports, any increase in tariffs could further complicate the already delicate balance of the US economy, which has been recovering from previous trade conflicts.
How might China respond to increased tariffs imposed by the US?
China could respond to increased tariffs by seeking alternative markets, strengthening ties with other countries, and ramping up efforts in sectors like technology and manufacturing to lessen dependency on the US. This could include enhancing trade relationships within the EU, Australia, and Southeast Asia.
What role do tariffs play in the ongoing trade war implications between the US and China?
Tariffs are a critical tool in the ongoing trade war, designed to alter trade balances and influence local economies. The imposition of new tariffs on China signifies a continuation of aggressive trade policies intended to protect American industries but may provoke counter-tariffs and complicate economic recovery on both sides.
Could increased China tariffs lead to supply chain disruptions in the US?
Yes, increased China tariffs could lead to significant supply chain disruptions as American companies may struggle to source components and products. This could lead to delays, increased manufacturing costs, and challenges in meeting consumer demand, adversely affecting various sectors of the economy.
What sectors in the US are most vulnerable to China tariffs?
Sectors such as technology, automotive, and consumer goods are particularly vulnerable to China tariffs. Companies relying on complex supply chains that include Chinese components may face higher costs, manufacturing delays, and pricing pressures in the US market.
How does the China economy stand to be affected by US tariffs?
The China economy may face setbacks as reduced exports to the US could lead to slower growth, job losses in manufacturing, and an overall negative impact on its global trade standing. Reduced demand from the US could also exacerbate existing economic challenges China is currently facing.
Are there alternatives for US businesses if China tariffs are imposed?
US businesses may look to diversify their supply chains by relocating production to countries like Vietnam, India, or even domestic sourcing, though these transitions require time and investment to develop appropriate manufacturing capabilities.
What is the significance of tariff policy in the context of global economic relations?
Tariff policy holds significant importance in shaping global economic relations as it affects trade balances, diplomatic ties, and international cooperation. High tariffs can lead to economic isolation, while lower tariffs may foster stronger partnerships and global market integration.
Can tariffs lead to a currency war between the US and China?
Yes, tariffs can provoke a currency war if nations attempt to weaken their currencies to counteract the impacts of tariffs on trade. Such actions complicate international trade dynamics and heighten tensions between economies, potentially leading to further conflict.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact on the U.S. Economy | Increased prices for consumers, potential supply-chain disruptions, and negative impacts on foreign relations. |
| Tariff Levels Proposed | 25% tariffs on goods from Mexico and Canada and 10% on Chinese imports with proposed tariffs going as high as 60%. |
| China’s Response Strategy | Concerns about the implications of these tariffs could lead to a tightening of relations with China’s allies. |
| Potential for Alternative Markets | China is looking to diversify markets through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative while fostering new partnerships. |
| Historical Context | Since the inception of tariffs in 2017, China’s share in U.S. imports has significantly declined, highlighting the impact of U.S. tariff policies. |
| Concerns Over Supply Chain Stability | The complexity of the existing supply chains makes it difficult for countries like India and Vietnam to completely fill the void left by China. |
Summary
China tariffs represent a significant factor in the ongoing economic discussions between the U.S. and China. While these tariffs may aim to pressure China’s economy, they could inadvertently backfire, generating higher costs for American consumers and straining international relationships. As countries react to these tariffs, the potential for redirection of trade alliances becomes a focal point, making it crucial for the U.S. to assess the broader implications of its trade policy.